Common algorithms list implemented Collections Framework
Java Collections Framework also provided polymorphic algorithms to operate on the collections. These are all reusable piece of functionality provided to make job easier when working with collections. All operation as usual defied static to call directly from Collections class. Below are algorithms list:
- Sorting
- Shuffling
- Routine Data Manipulation
- Searching
- Composition
- Finding Extreme Values
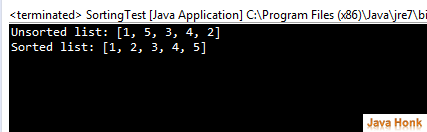
Sorting: Collections class sort algorithm reorders the List in ascending order according to an ordering relationship. There is two forms of operation has been provided. Simple form takes the parameter List and sorts it out according to its elements natural ordering. Please see example below:
package com.javahonk.algorithms; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class SortingTest { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(1); list.add(5); list.add(3); list.add(4); list.add(2); System.out.println("Unsorted list: " + list); Collections.sort(list); System.out.println("Sorted list: " + list); } }
Output:
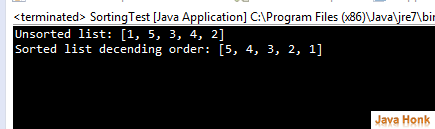
Sorting second form of sort accepts Comparator as parameter in addition to List and sorts elements with Comparator. Let’s suppose we want to print above example in reverse order of size. Below example will show you how to achieve this:
package com.javahonk.algorithms; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; public class SortingTest implements Comparator<Integer> { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(1); list.add(5); list.add(3); list.add(4); list.add(2); System.out.println("Unsorted list: " + list); // Sort list in decending order Collections.sort(list, new SortingTest()); System.out.println("Sorted list decending order: " + list); } @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o2.intValue() - o1.intValue(); } }
Output:
Shuffling: Shuffle algorithm does the opposite of what sorting does as you see above example it will destroy any trace of order that could have been present in List. This algorithm reorders List based on input from source of randomness such a way all possible permutations will occur with equal likelihood. This algorithm is very useful in implementing games of chance. Please see example here
Routine Data Manipulation: Java Collections class gives five algorithms for implementing routine data manipulation on a List objects all of which shown below:
- reverse – It reverses the order of elements in List
- Fill – This overwrites each and every element in List with specified value.
- copy – It takes two arguments first is destination List and second is source List and it will copies elements of source into destination and overwrite its contents. Destination List should be at least as long as the source is. If it will be longer, remaining elements in the destination List are unaffected.
- swap — It swaps elements at the listed positions in a List.
- addAll — It adds all specified elements into Collection. The elements which will be added could be specified individually or as array.
Searching: Search algorithm searches on a specified element of a given sorted List. Search algorithm got two forms. First one takes List and element that will be search for also called “search key”. Basically this algorithm assumes that the given List have sorted in ascending order because of the natural ordering of its elements. Second one takes Comparator which is extra in addition to List and “search key”, and again assumes that List is sorted into ascending order because of specified Comparator.
Composition: It uses frequency and disjoint algorithms to test certain aspect of composition of one or more given Collections objects:
- Frequency – This counts number of times when specified element occurs on the specified collection
- disjoint – This algorithm determines whether given two Collections objects are disjoint i.e. whether they have contain no elements in the object which is common
Finding Extreme Values: This returns min and the max algorithms respectively. The maximum minimum element contained in a specified Collection object. Both min and max operations comes in the two forms. The first form takes only a Collection object and returns minimum or maximum element according to its ordering. The second form takes Collection and Comparator which is in addition to Collection object from frist form and returns minimum or maximum element based on the specified Comparator.