What is local member and class variable
Answer : Java variable is basically use as unit of storage in program. A variable is defined by the combination of type, identifier and an optional initializer. When we define the variables the they all have a scope, which defines their visibility, and a lifetime.
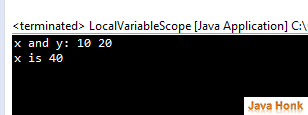
Local variable : In java local variable is a variable that is given local scope. Only the method where the parameter appears can access these variables. These variables are used to store intermediate results. Please see example below:
public class LocalVariableScope { public static void main(String[] args) { int x; // known to all code within main x = 10; if (x == 10) { // start new scope int y = 20; // known only to this block // x and y both known here. System.out.println("x and y: " + x + " " + y); x = y * 2; } // y = 100; // Error! y not known here // x is still known here. System.out.println("x is " + x); } }
instance variable (Member variable) : In java an instance variable is a variable defined inside a class (i.e. a member variable), for which each object of the class has a separate copy, or instance. For see example below:
public class InstatnceVariable { // member variable - a new instance // of this variable will be created for each // new instance of InstatnceVariable class. // The lifespan of this variable is equal // to the lifespan of "this" instance of InstatnceVariable. int i; }
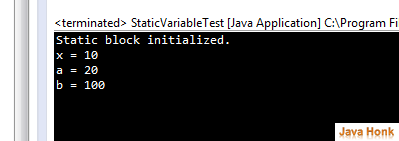
Static variable (Class variable) : Static member also called class member and to create it precede its declaration with the keyword static.When a member is declared static, it can be accessed before any objects of its class are created and without reference to any object. Good example of a static member is main( ). main( ) is declared as static because it must be called before any objects exist. Instance declared as static are also callled global variables When objects of class are created no copy of a static variable is made. Instead, all instances of the class share the same static variable. Please see example below:
package com.javahonk.staticTest; public class StaticVariableTest { static int a = 20; static int b; static void methodStaticForTest(int x) { System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("a = " + a); System.out.println("b = " + b); } static { System.out.println("Static block initialized."); b = a * 5; } public static void main(String[] args) { methodStaticForTest(10); } }