What is stack and queue ?
Answer : Please see difference below:
| Stack | Queue |
| Stack class represents and works on last-in-first-out (LIFO) manner on its stack of objects | Queue class represents and works on first-in-first-out (FIFO) manner on its order elements |
| Here vector has been treated as a stack | Here collection is designed to hold the object |
| It extends Vector class | It extends Collection class |
| Items insertion deletion happens and only one end that is “Top of the stack” | Here items insert from the back and deleted from the front |
| Stack is collection of objects accumulated on top | It’s ordered collections of the objects |
| Stack is a list | Queue is a collection |
Stack example:
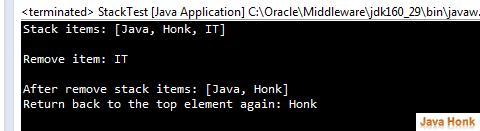
package com.javahonk.queuetest; import java.util.Stack; public class StackTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); stack.push("Java"); stack.push("Honk"); stack.push("IT"); System.out.println("Stack items: " + stack); System.out.println("\nRemove item: "+ stack.pop()); System.out.println("\nAfter remove stack items: " + stack); System.out.println("Return back to the top element again: " + stack.peek()); } }
Output:
Queue example:
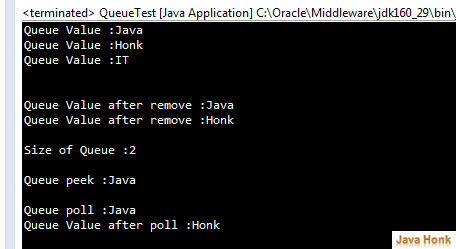
package com.javahonk.queuetest; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class QueueTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>(); queue.add("Java"); queue.add("Honk"); queue.add("IT"); Iterator<String> iterator = queue.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { String string = (String) iterator.next(); System.out.println("Queue Value :" + string); } System.out.println("\n"); // Remove element form queue queue.remove("IT"); Iterator<String> iteratorRemove = queue.iterator(); while (iteratorRemove.hasNext()) { String string = (String) iteratorRemove.next(); System.out.println("Queue Value after remove :" + string); } //Size of the queue System.out.println("\nSize of Queue :" + queue.size()); // Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of // this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. System.out.println("\nQueue peek :" + queue.peek()); // Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, // or returns null if this queue is empty. System.out.println("\nQueue poll :" + queue.poll()); //After poll method call retrive value again Iterator<String> iteratorPoll = queue.iterator(); while (iteratorPoll.hasNext()) { String string = (String) iteratorPoll.next(); System.out.println("Queue Value after poll :" + string); } } }
Output: