Difference between ArrayList HashMap
Answer: Below are differences:
| ArrayList | HashMap |
| ArrayList implements List interface (public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable) | HashMap implements Map interface (public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable) |
| It works on collection of object and objects can be added to ArrayList using add method | It works on collection of object with key-value pair and object can be added using put method |
| It allows null values and can be added to the list multiple times because it appends specified element to end of the list | HashMap also allows null as key or value but duplicate key not allowed |
| ArrayList is roughly equivalent to the Vector class except that this class is unsynchronized | HashMap class is roughly equivalent to the Hashtable except that this class unsynchronized and also permits nulls |
| Whenever elements added to ArrayList its capacity grows automatically and details of growth policy are not specified. | HashMap default load factor is .75 means it grows by .75 by its initial size which can be control by its constructor |
Please have example java class:
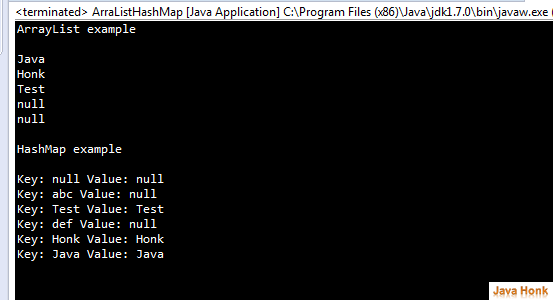
package com.javahonk.arraylistmap; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; public class ArraListHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("ArrayList example\n"); List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("Java"); list.add("Honk"); list.add("Test"); list.add(null); list.add(null); for (String string : list) { System.out.println(string); } System.out.println("\nHashMap example\n"); HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); hashMap.put("Java", "Java"); hashMap.put("Honk", "Honk"); hashMap.put("Test", "Test"); hashMap.put("Test", "Test"); hashMap.put(null,null); hashMap.put("abc",null); hashMap.put("def",null); Set<Entry<String, String>> set = hashMap.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, String> entry : set) { System.out.println("Key: "+entry.getKey() +" Value: "+entry.getValue()); } } }