Difference between Hash map and Hash table
Answer: Below are differences:
| HashMap | HashTable |
| HashMap is not synchronized | It is synchronized(All method are thread safe) |
| HashMap cannot shared between multiple thread without doing proper synchronization of the method | HashTable is thread safe and without any hesitation It can be shared between multiple thread |
| HashMap is fast because methods are not synchronzied | HashTable is much slower than due to its synchronized feature, it means to perform any task it has to acquire lock of the object while others need to wait to release the lock. |
| HashMap allows null value as key | HashTable doesn’t allows null as key |
| Iterator in the HashMap is fail fast and it throws exception if some other thread modify it. | But enumerator of on the HashTable not throw this exception if any other thread modify the map structurally |
| HashMap is better for non-threaded application | Whereas HashTable is better for threaded application where multiple thread use common resources |
| Also HashMap sub classed is LinkedHashMap which provides predictable iteration order and can be easily switch out for LinkedHahsMap | Using HashTable this functionality wouldn’t be easy |
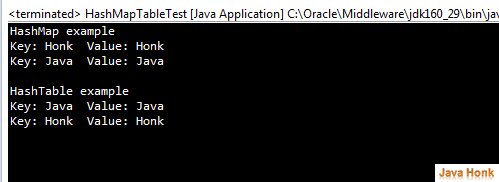
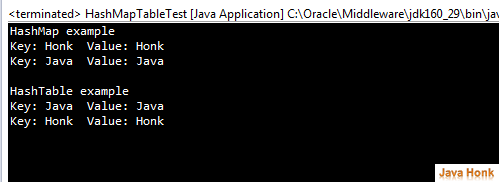
Please see java example below of HashMap and HashTable:
package com.javahonk.hashmaptable; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Hashtable; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; public class HashMapTableTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("Java", "Java"); map.put("Honk", "Honk"); System.out.println("HashMap example"); Iterator<Entry<String, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String,String> entry = (Map.Entry<String,String>) it.next(); String key = (String) entry.getKey(); String val = (String) entry.getValue(); System.out.println("Key: " + key + " Value: " + val); } System.out.println("\nHashTable example"); Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<String, String>(); hashtable.put("Java", "Java"); hashtable.put("Honk", "Honk"); Enumeration<String> enumeration = hashtable.keys(); while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) { String value = (String) enumeration.nextElement(); System.out.println("Key: "+value +" Value: "+hashtable.get(value)); } } }
Output: