Read File Java six different ways
In below sample code you will see how to read file using java. Here you will see six different ways to read small and large file using latest Java API.
Java example code:
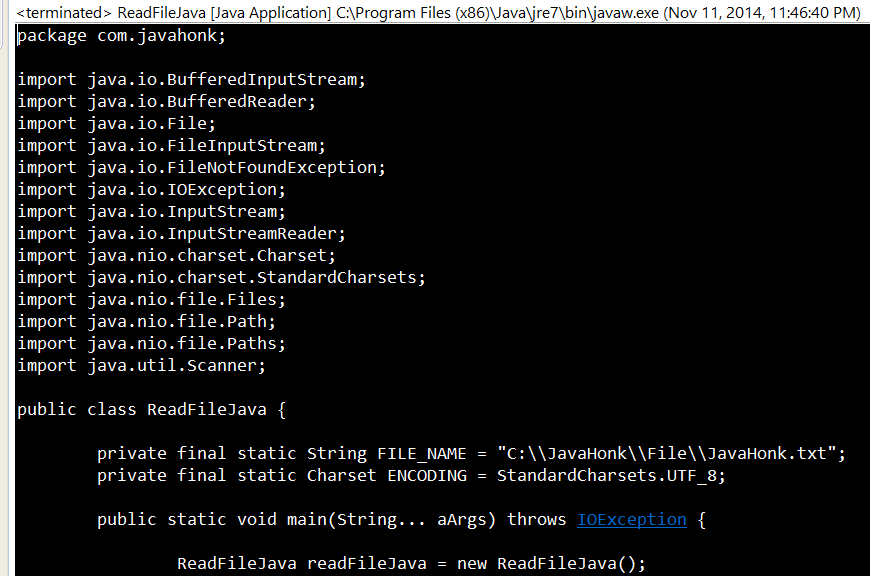
package com.javahonk;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadFileJava {
private final static String FILE_NAME = "C:\\JavaHonk\\File\\JavaHonk.txt";
private final static Charset ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
ReadFileJava readFileJava = new ReadFileJava();
//Read File Using Stream I/O
readFileUsingStreamIO();
//Read file using Buffered Stream I/O
readFileUsingBufferedStreamIO();
//Read large file Using BufferedInputStream
readFileUsingBufferedInputStream();
//Read small file
readFileJava.readSmallFile(FILE_NAME);
//Read large file
readFileJava.readLargeFile(FILE_NAME);
//Read large file another example
readFileJava.readLargeFileAnotherExample(FILE_NAME);
}
private static void readFileUsingStreamIO() {
Path file = Paths.get(FILE_NAME);
try (InputStream in = Files.newInputStream(file);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in))) {
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException ioException) {
System.err.println(ioException);
}
}
private static void readFileUsingBufferedStreamIO() {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("US-ASCII");
try (BufferedReader reader = Files.newBufferedReader(Paths.get(FILE_NAME), charset)) {
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException ioException) {
System.err.format("IOException: ", ioException);
}
}
private static void readFileUsingBufferedInputStream()
throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_NAME);
BufferedInputStream bin = null;
// create FileInputStream object
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file);
// create object of BufferedInputStream
bin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);
// read file
while (bin.available() > 0) {
System.out.print((char) bin.read());
}
bin.close();
}
private void readSmallFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
writeOutputOnConsole(Files.readAllLines(path, ENCODING));
}
private void readLargeFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(path, ENCODING.name())) {
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
writeOutputOnConsole(scanner.nextLine());
}
}
}
private void readLargeFileAnotherExample(String fileName)
throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
try (BufferedReader bufferedReader = Files.newBufferedReader(path, ENCODING)) {
String line = null;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
writeOutputOnConsole(line);
}
}
}
private static void writeOutputOnConsole(Object value) {
System.out.println(String.valueOf(value));
}
}
Output:
For more information read file using java please refer this oracle documentation here