The Shuffling algorithm does the opposite of what sort does, destroying any trace of order that may have been present in a List. That is, this algorithm reorders the List based on input from a source of randomness such that all possible permutations occur with equal likelihood, assuming a fair source of randomness. Shuffling algorithm is useful in implementing games of chance. For example, it could be used to Shuffling a List of Card objects representing a deck. Also, it’s useful for generating test cases.
This operation has two forms: one takes a List and uses a default source of randomness, and the other requires the caller to provide a Random object to use as a source of randomness. The Shuffling code for this algorithm shown in an example below using java.
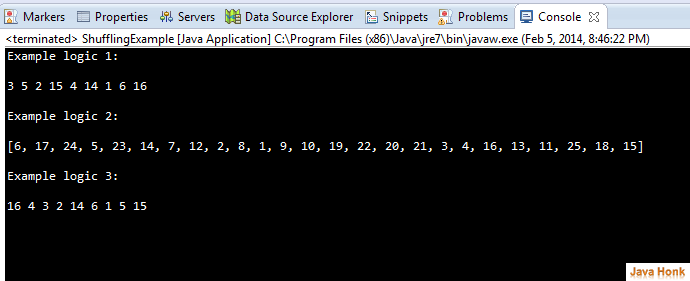
package com.javahonk; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Random; public class ShufflingExample { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("Example logic 1: \n"); int[] solutionArray = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 16, 15, 14 }; shuffleArray(solutionArray); for (int i = 0; i < solutionArray.length; i++) { System.out.print(solutionArray[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("\nExample logic 2: \n"); ArrayList<Integer> cards = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i=1;i<=25;i++) { cards.add(i); } Collections.shuffle(cards); System.out.println(cards); System.out.println("\nExample logic 3: \n"); shuffleArray2(solutionArray); for (int i = 0; i < solutionArray.length; i++) { System.out.print(solutionArray[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); } static void shuffleArray(int[] solutionArray) { Random rnd = new Random(); for (int i = solutionArray.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { int index = rnd.nextInt(i + 1); // Simple swap int a = solutionArray[index]; solutionArray[index] = solutionArray[i]; solutionArray[i] = a; } } static void shuffleArray2(int[] array) { int index; Random random = new Random(); for (int i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { index = random.nextInt(i + 1); if (index != i) { array[index] ^= array[i]; array[i] ^= array[index]; array[index] ^= array[i]; } } } }
Output: