Stack Java example
public class Stack extends Vector
Stack represents last-in-first-out (LIFO) of objects. This extends Vector class includes five operations which allow vector also treated as stack. Its push operation push object in stack, pop operations remove the object from stack and peek operation returns top value on stack. Its method empty is to test if stack is empty or not and method search returns how far the object in the stack from top.
Deque class is preferable compare to stack because it has consistent and complete set of LIFO operations has provided.
Example Stack test java class:
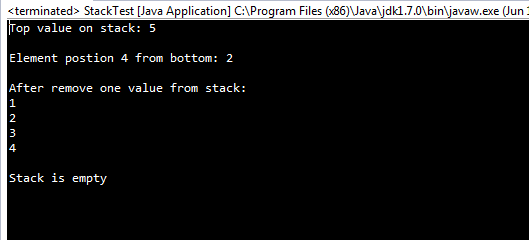
package com.javahonk.action; import java.util.Stack; public class StackTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { stack.push(i); } //Print top value on stack System.out.println("Top value on stack: "+stack.peek()); //Search element position on stack int positionOfElement = stack.search(4); System.out.println("\nElement postion 4 from bottom: " +positionOfElement); //Remove single element from stack stack.pop(); System.out.println("\nAfter remove one value from stack:"); //Print value after removes for (Integer integer : stack) { System.out.println(integer); } //Remove all element from stack while (!stack.empty()) { stack.pop(); } // Print value if(stack.empty()) System.out.println("\nStack is empty"); } }
Output: