State Pattern
The state pattern, which closely resembles Strategy Pattern, is a behavioral software design pattern, alsoknown as the objects for states pattern. This pattern is used in computer programming to represent the state of an object. This is a clean way for an object to partially change its type at runtime
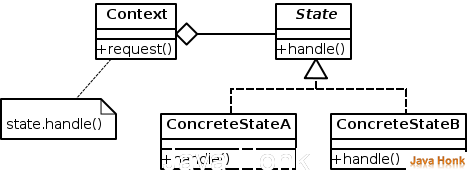
Structure Diagram :
Example: The state interface and two implementations. The state’s method has a reference to the context object and is able to change its state.
State interface :
public interface State { void writeName(StateContext stateContext, String name); }
Class StateA :
public class StateA implements State { public void writeName(StateContext stateContext, String name) { System.out.println(name.toLowerCase()); stateContext.setState(new StateB()); } }
Class StateB
public class StateB implements State { private int count = 0; public void writeName(StateContext stateContext, String name) { System.out.println(name.toUpperCase()); // change state after StateB's writeName() gets invoked twice if (++count > 1) { stateContext.setState(new StateA()); } } }
The context class has a state variable which it instantiates in an initial state, in this case StateA. In its method, it uses the corresponding methods of the state object.
public class StateContext { private State myState; public StateContext() { setState(new StateA()); } // normally only called by classes implementing the State interface public void setState(State newState) { this.myState = newState; } public void writeName(String name) { this.myState.writeName(this, name); } }
Main class for test:
public class TestClientState { public static void main(String[] args) { StateContext sc = new StateContext(); sc.writeName("Monday"); sc.writeName("Tuesday"); sc.writeName("Wednesday"); sc.writeName("Thursday"); sc.writeName("Saturday"); sc.writeName("Sunday"); } }